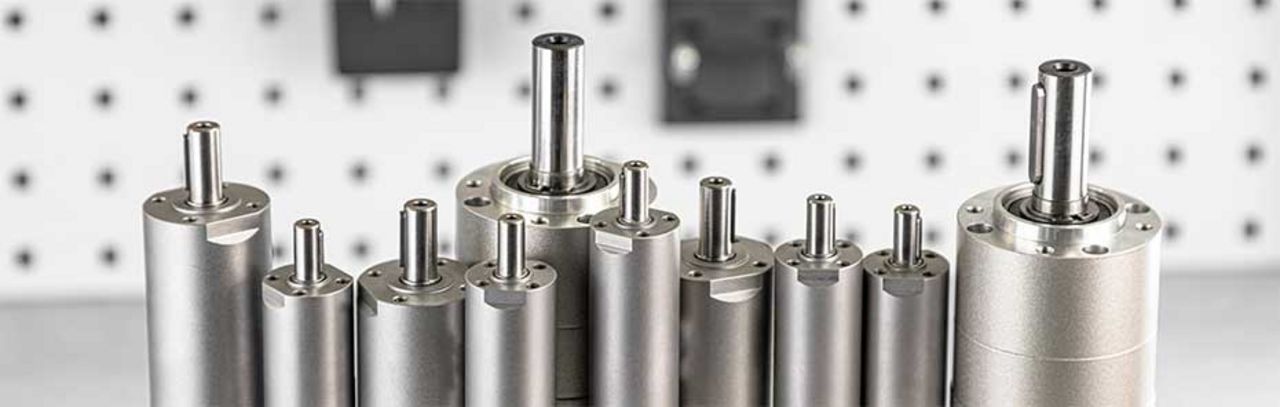
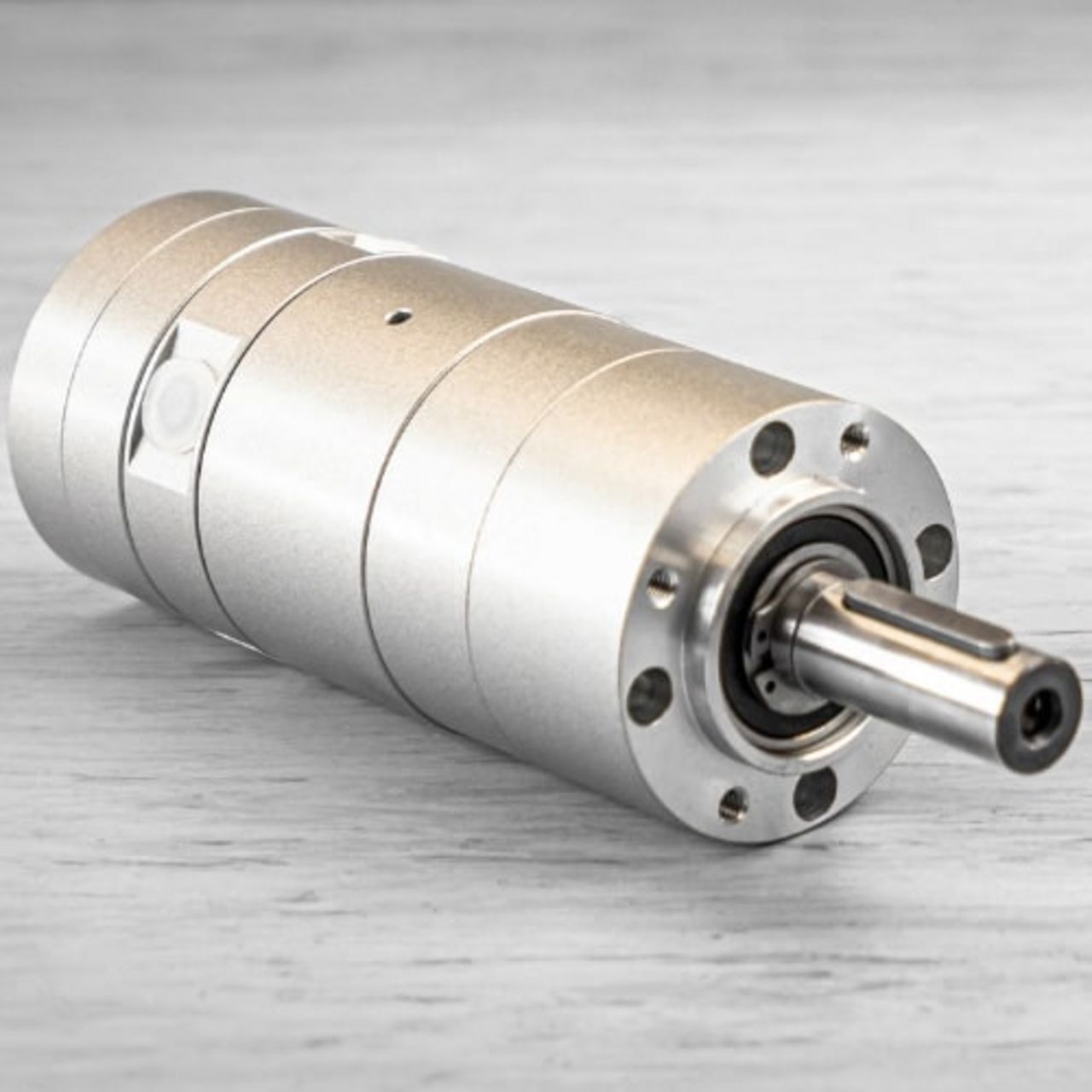
What is an air motor?
Air motors are safe and robust drive systems, which are used in areas where an overload-safe and powerful drive is needed, especially in such areas where conventional drive technology cannot continue to rotate. An air motor is used according to your individual application, such as:
- an oil-free, sealed, and insensitive to cleaning solvent especially for the food industry.
- a sterilizable air motor for the medical technology.
- an air motor for specialized applications such as our drainage-milling robot.
- our ATEX-compliant total systems – including air motor, brake and gearing, are ready to be used in explosion hazardous environments.
We select for you the most economical and the safest drive solution that best fits your application, no matter if the solution is an air motor from our catalog program or if it is a complex customized system.
TIP: Our guide to selecting air motors
Automation is defined by efficiency and high pressure to keep costs low. Engineers and designers in the machine and equipment building industry have many questions in regards to the layout of their machines. Selecting the particular drive system for your application is the main focus. Air motors are uncomplicated and robust drives, which can be used in a wide variety of application areas. This guide offers extensive technical information to support you when selecting the drive type, the material, the calculation of a suitable air motor, and its intergration in to your system.
Step by step, this guide will lead you through the application conditions that would influence on the lifespan, power and performance of your air motor. This guide will take the information you input and summarize it so that it can be sent to us for an inquiry.
If you prefer not to use the online guide then you can still download the complete form with all technical information right here:
Areas of application for air motors
Air motors are a fascinating and innovative technology that converts air pressure into mechanical energy. As an environmentally friendly drive solution, they have become increasingly popular in recent years and offer a wide range of benefits for various applications.
FAQ & technical information on the air motor
Air motors work according to a simple principle. The compressed air generated by the compressor causes the motor to rotate. Vane motors, turbines and gear motors differ in terms of their design and specific areas of application.
The wide range of application variants, the simple design, the low power-to-weight ratio, the wide speed range and the explosion safety ensure that the air motor can be used in a wide range of applications. Our air motors are used in almost all industrial sectors:
- Automotive industry
- Food industry
- Foundries
- Medical sector
- Shipbuilding
- Chemical industry
- Paper industry
In addition to numerous standard motors, we manufacture air motors flexibly and at an attractive price-performance ratio for your individual application.
Pneumatic motors are safe and robust drive systems, that are used when a powerful and overload-safe drive is required.
- Safe – for use in potentially explosive environments
- Sealed– for the use underwater (submerged)
- Cleaning Agent Resistant – and suitable for food industry demands
- Sterilizable– for repeated use in cleanrooms
- Light Weight and Compact– only 1/5th of the mass and 1/3rd of the size of an comparable electric motor
- Overload Safe– can be loaded until standstill without damage
- Reversible– can be set in both rotational directions
- Easy to Control – smootly controlled by altering the pressure or air quantity (throttling)
- Acid Insensitive
- Vibration Insensitive
- Heat Insensitive
- Dust Insensitive
- Air Connections: If you connect your air-motor, do not close the secondary inlet-connection (reverse port) and the exhaust port. This allows your motor to start unimpeded.
Alternatively you can use the certified DEPRAG silencers for sound reduction.
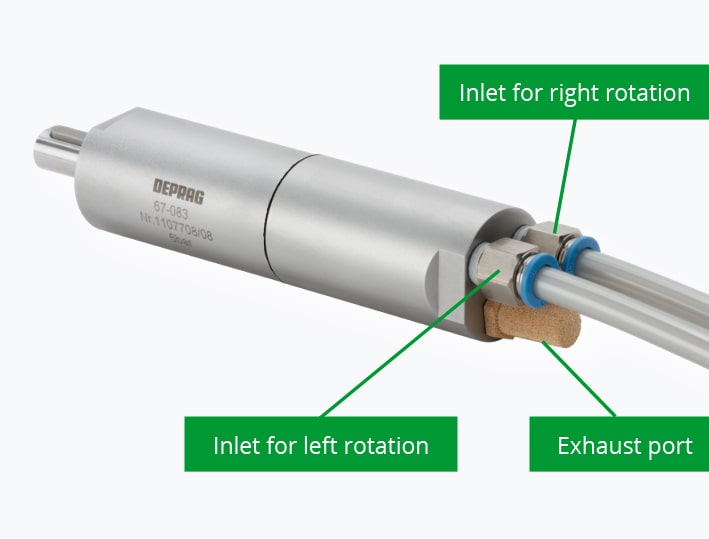
- Connection Fittings and Operating Pressure: Air distributors, pneumatic valves, quick couplers and air hoses can often be specified with too small a cross section. This has a direct influence on the performance of your compressed air motor. A pressure drop of 1 bar results already into a performance reduction of 23%. Only with a sustained pressure of 6 bar directly to the inlet port can the air motor deliver the specified power. The minimum requirement for the suitable hose ID is shown for every motor in our product catalog.
Example: BASIC LINE Air Motor with 90 W power PDF Product Catalog D 6200): The minimum required flow diameter for all connection fittings is 13 mm.
- Air Quality: Keeping the recommended air quality: dry, particle free inlet air. The optimum longevity and maximum power output is achieved by oiling the motor using oils free of resin and acid. One to two drops of oil per cubic meter of compressed air is all that is required to lubricate your airmotor.
DEPRAG airmotors of the BASIC LINE and ADVANCED LINE are also suitable for oilfree operation. However, a resulting power penalty of approximately 15% should be taken into consideration. - Connection Control Diagrams for the Control of our Airmotors: To control an airmotor in one direction a simple 2/2-way valve is all that is needed.
Airmotors that are reversible (i.e. into two turn directions), can also be controlled by a simple flow valve, if the motor contains an integrated, manual reverse lever (for example: POWER LINE high performance motors).
Otherwise, a 5/3-way valve or alternatively two 3/2-way valves are needed, so that the unused inlet can be exhausted.When using any valves, make sure to pay attention to the minimum required hose ID and that the valve allows for the a sufficient flow rate as shown for each motor in our product catalog.
If the airmotor is used in one turn direction only, then operated it with a 2/2-way valve: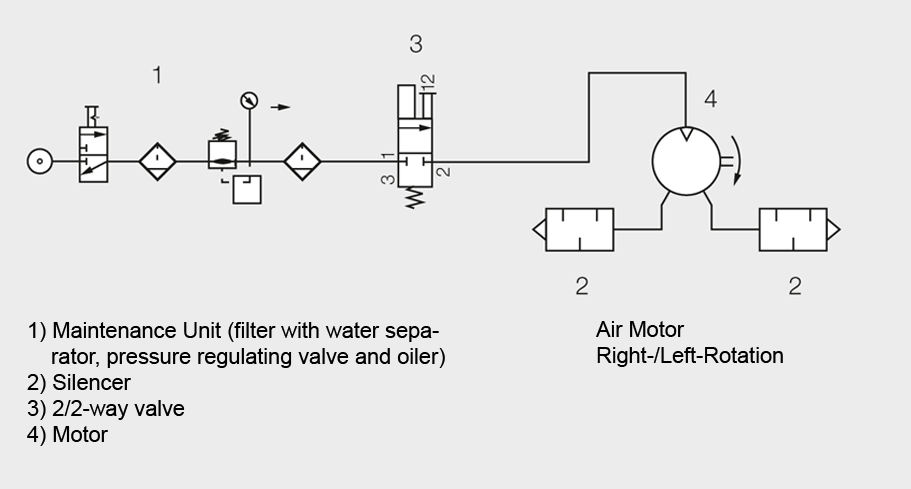
If the motor needs to be used with reverse, then it should be operated with a 5/3-way valve: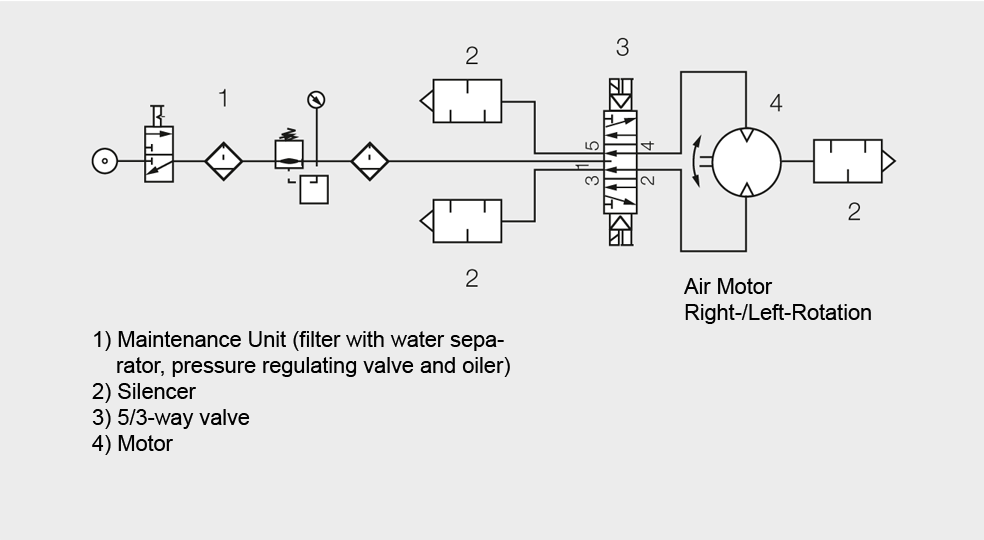
The airmotor can also be used with two 3/2-way valves if operated with reverse: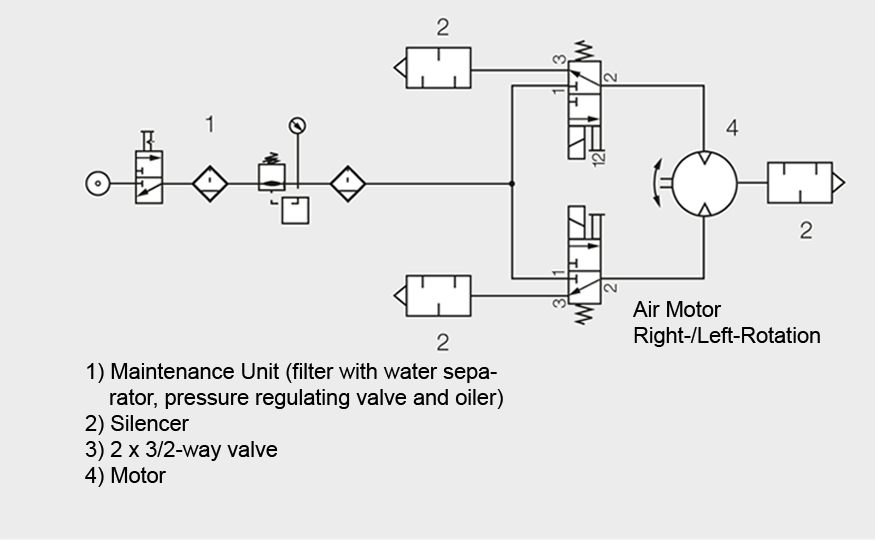
Infinite variable regulation of the air pressure or air volume
Your airmotor is very flexible: The speed can be adjusted to fit your requirements!
Speed change can be achieved by varying the air pressure, changing the air volume or more commonly by a combined regulation of air pressure and air volume.
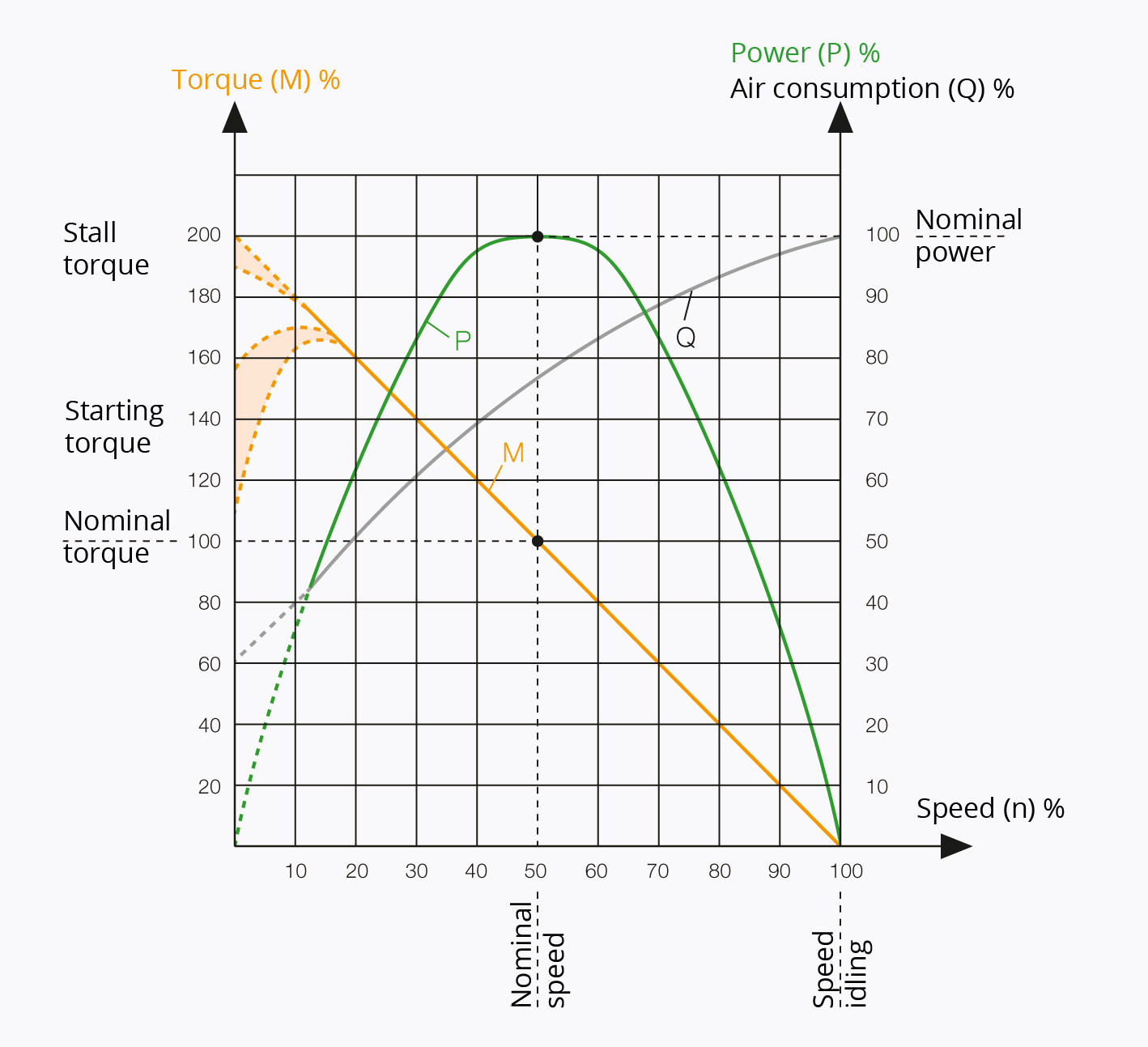
- Speed change through load change: The speed of the airmotor automatically adapts to the load changes. This means that unloaded, the airmotor operates at idle speed. If there is increased load (low torque) the nominal speed is close to the idle speed. With increased load (increased torque), the speed decreases.
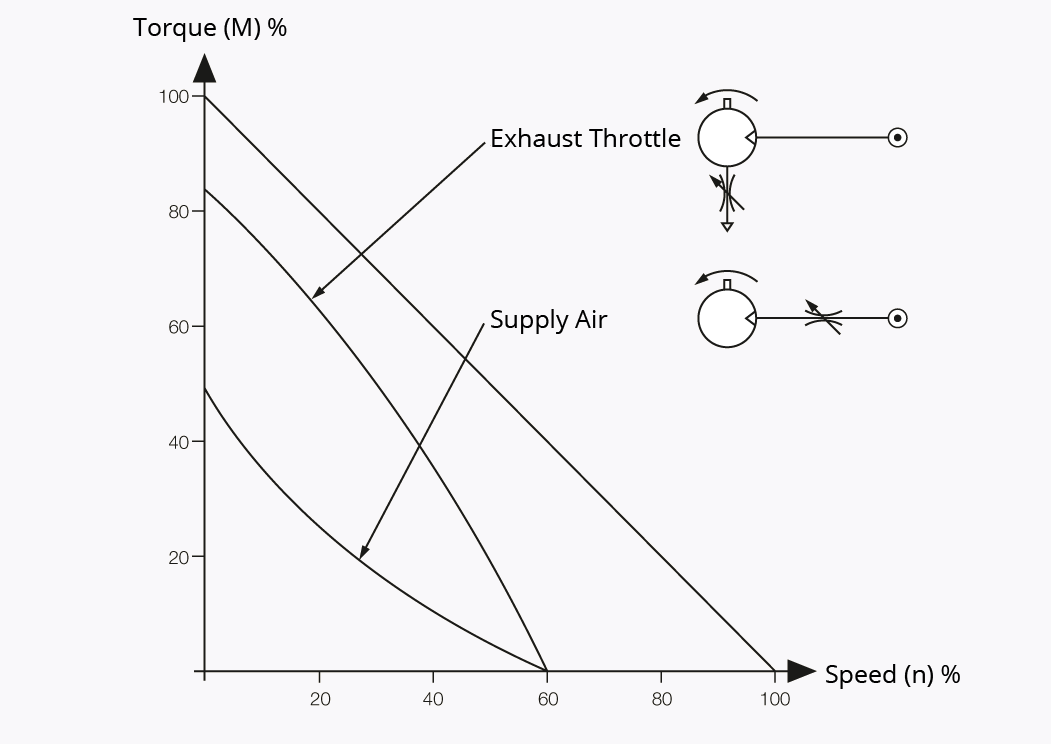
- Regulating the speed by air volume: Through throttling the exhaust air, a speed reduction of the pneumatic motor is achieved without any considerable loss of performance or torque. If you would like to reduce the power output or the torque in addition to the speed, then an air inflow throttle is recommended.
- Regulating the speed by air pressure: The operating data of the DEPRAG airmotor is based on an operating air pressure of 6 bar. By adjusting the pressure in the range of 4 to 6.3 bars you can manipulate the speed, power, torque and air consumption of your pneumatic motor without problems.
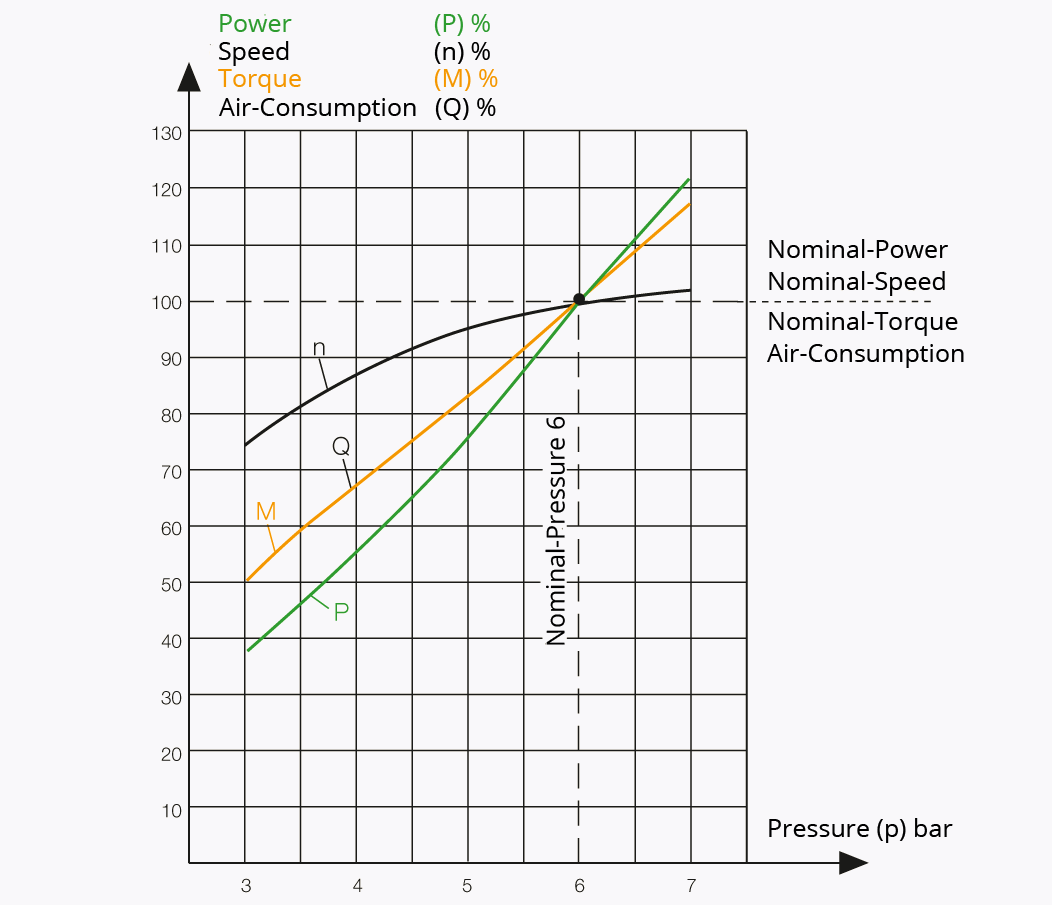
The following correctional factors are applicable to achieve the desired adaptation: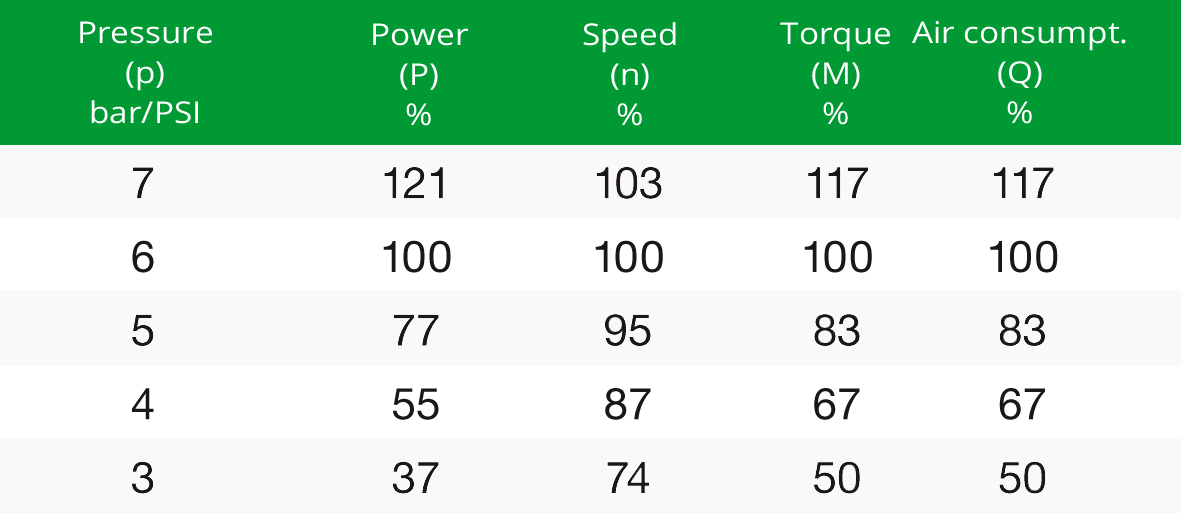
- Energy Efficiency: An pneumatic motor achieves its maximum power when it is operating as close as possible to its rated speed (50% of the rated idle speed). The energy balance is best in this area because the compressed air is used efficiently.
Service for your air motor
Beginning with the optimal layout of your air motor and including the comprehensive performance testing of existing drives, we also offer our customer an extensive service package. We are happy to take on the regular maintenance or repair of your air motor for you. Special response times can also be arranged if required. You can also benefit from our comprehensive training program: